Many girls lack the knowledge, confidence, facilities and materials needed to manage periods safely and with dignity. Improving menstrual health not only has immediate benefits to their wellbeing, but can lead to long-term improvements to women’s education, health and development.
MENISCUS is led by Professor Helen Weiss, Director of the MRC International Statistics & Epidemiology Group at LSHTM in partnership with the MRC/UVRI & LSHTM Uganda Research Unit, WoMena Uganda, Makerere University Uganda and University College London.
The aim of the MENISCUS trial is to assess whether the intervention improves educational attainment, mental health symptoms, menstrual management and quality of life outcomes among girls in secondary school in Uganda.
Background
Many girls lack basic knowledge, facilities and/or materials for managing menstruation safely and with dignity. Improving menstrual health can lead to sustained, long-term benefits to education, health and development. Though many governmental and non-governmental organisations are interested in introducing interventions to improve menstrual health, there is a lack of evidence to guide policies and ensure interventions are effective.
Our previous studies have shown that poor menstrual health is associated with anxiety among girls and with missing secondary school or class in Wakiso District Uganda. An effective intervention needs to be holistic, and address not only lack of knowledge of puberty and menstruation, but also the social environment (to reduce stigma) and training in practical methods to enable girls to better manage their periods i.e. provision and training in use of period products, education about effective pain management, and improvements to school sanitation facilities. Our studies suggest that an intervention addressing these elements can potentially improve education and mental health outcomes, but a randomised controlled trial is needed for definitive results to drive forward policy changes.
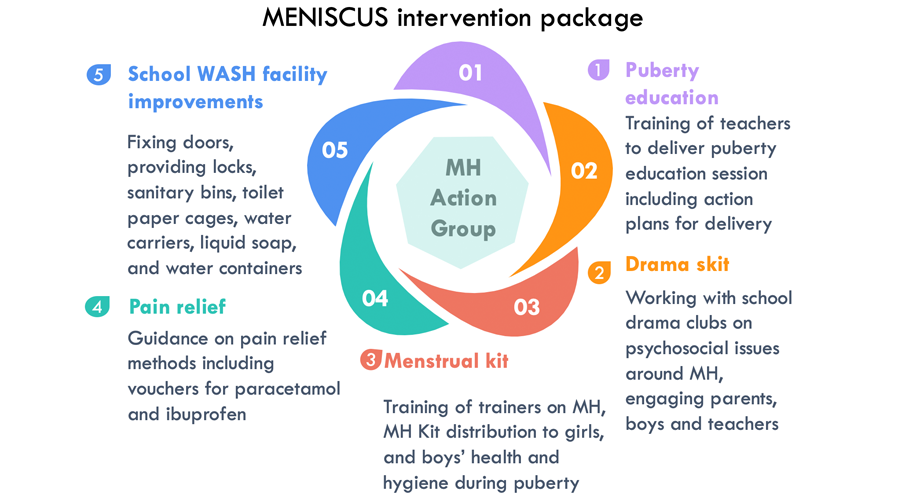
The intervention
The MENISCUS intervention was developed with teachers and schools and was successfully piloted in two schools in 2017-2018. It is a multi-component intervention and involves:
- Training teachers to provide puberty education to boys and girls
- Working with school drama clubs to tackle menstrual health issues, with performances to parents and teachers.
- Providing menstrual kits, including a supply of re-usable pads and optional menstrual cups with training on their use.
- Providing strategies for pain management, including vouchers for pain relief medication.
- Simple upgrades to school toilets, including providing items such as bins and soap, and repairing locks.
- Establishing a menstrual health action group at each school to oversee the delivery of the intervention.
Trial Design
We are evaluating the impact of the intervention through a cluster-randomised trial. A total of 60 secondary schools in Wakiso and Kalungu districts were randomised, so that 30 schools received the MENISCUS intervention in 2022, and 30 received optimised usual care (provision of Government Menstrual Health guidelines and other relevant printed materials). At the end of the trial, schools in the control arm will be offered the intervention package.
The primary outcomes are i) examination performance based on the curriculum taught during the intervention year; and ii) mental health symptoms including emotional symptoms, attention and peer relationship problems.
We will also assess the impact of the intervention on other outcomes including (in both girls and boys) menstrual knowledge and attitudes; and (in girls only) menstrual practices, pain management, self-efficacy to manage menstruation, quality of life, prevalence of urinary tract infections, school and class attendance, and confidence in science and maths. The outcomes will be compared between the intervention and control arms after one year, adjusting for baseline measures.
Impact
The MENISCUS intervention is novel in several ways. It will be the first to:
- Be truly multi-component, not focusing primarily on either education, provision of pads, or improvement of toilet facilities;
- Address pain management, a major reason for school absence in girls;
- Focus on boys as well as girls, enabling us to address stigma and improve the school environment; and
- Include secondary schools in both rural and peri-urban areas, as most previous studies have been in primary schools in rural areas.
The intervention has been designed to be culturally appropriate, aligned with Government guidelines, cost-effective, environmentally-friendly and practically sustainable within the schools. We will assess these elements through a process evaluation, health economics component and policy analysis.
Our intention is that the MENISCUS trial will provide needed evidence to guide the rapidly growing community of implementing partners working to improve menstrual health globally. We will share findings with local, national and international stakeholders through a workshop and meetings so that the intervention can be scaled-up as appropriate.
Funding
The MENISCUS trial is supported by the Joint Global Health Scheme with funding from the UK Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office, the UK Medical Research Council, the UK Department of Health and Social Care through the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) and Wellcome (grant ref MR/V005634/1).
The MENISCUS trial is led by scientists at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and MRC/UVRI and LSHTM Uganda Research Unit, in collaboration with implementing partner WoMena Uganda, Makerere University, and University College London.
Principal Investigator
Helen Weiss, Professor of Epidemiology, LSHTM
Co-Investigators
- Chris Bonell, Professor of Public Health Sociology, LSHTM
- Giulia Greco, Associate Professor in Health and Wellbeing Economics, LSHTM
- John Jerrim, Professor of Education and Social Statistics, UCL Institute of Education
- Catherine Kansiime, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Nambusi Kyegombe, Head of Social Science Programme, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Stephen Lagony, Trial Manager, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Fred Matovu, Senior Lecturer and Director, PADRI, Makerere University
- Stella Neema, Associate Professor of Medical Anthropology, Makerere University
- Kate Nelson, Research Fellow in Epidemiology, LSHTM
- Janet Seeley, Professor of Anthropology and Health, LSHTM
- Clare Tanton, Assistant Professor in Epidemiology, LSHTM
- Belen Torondel, Professor, LSHTM
Research team
- Connie Alezuyo, Coordinator, Education Response Plan Secretariat, MoES
- Robert Bakanoma, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Christopher Baleke, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Ratifah Batussa, Data Manager, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Levicatus Mugenyi, Statistician, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Alex Mutazindwa, Study Administrator, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Rodah Nambi, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Prossy Namirembe, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Beatrice Nanyonga, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Denis Ndekezi, Social Scientist, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Titus Ssesanga Kisa, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
- Katherine Thomas, Research Assistant, LSHTM
- Aggrey Tumuhimbise, Research Team Lead, MRC/UVRI & LSHTM
Implementing partner
- WoMena Uganda
Trial registration:
Parent/Guardian Information Sheets
Trial information sheet for parent/guardian of female student (English)
Trial information sheet for parent/guardian of female student (Luganda)
Menstrual cup information sheet for parent/guardian of female student (English)
Menstrual cup information sheet for parent/guardian of female student (Luganda)
Participant Information Videos
Trial and menstrual cup informational video A (English)
Trial and menstrual cup informational video A (Luganda)
Trial informational video (English)
Trial informational video (Luganda)
Male student informational video (English)
Male student informational video (Luganda)
The MENISCUS trial: Findings from a menstrual health intervention trial in Ugandan secondary schools
Menstrual health is a human right. In this video, we summarise findings from the MENISCUS trial evaluating the effectiveness of a multi-component menstrual health intervention on mental health, education and menstrual health in Ugandan schools.
Produced by: Ardent Creative (ardentc.com)
MENISCUS Trial Publications
Kansiime C, Hytti L, Nelson KA, Torondel B, Francis SC, Tanton C, et al. Menstrual health interventions, schooling, and mental health problems among Ugandan students (MENISCUS): study protocol for a school-based cluster-randomised trial. Trials. 2022 Sep 7;23(1):759. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06672-4
Ssemata AS, Ndekezi D, Kansiime C, Bakanoma R, Tanton C, Nelson KA, Hytti L, Neema S, Tornodel B, Seeley J, Weiss HA, MENISCUS Group. Understanding the social and physical menstrual health environment of secondary schools in Uganda: a qualitative methods study. [Under review]
MENISCUS presentations
LSHTM Global Health Lecture Series 2023: Why Menstrual health and hygiene matters?
Aberdeen Centre for Women’s Health: International Women’s Day 2022 Research Seminar
MENISCUS-2 Pilot Study
Kansiime C, Hytti L, Nalugya R, et al. Menstrual health intervention and school attendance in Uganda (MENISCUS-2): a pilot intervention study. BMJ Open 2020;10:e031182. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031182
Nalugya, R., Tanton, C., Hytti, L. et al. Assessing the effectiveness of a comprehensive menstrual health intervention program in Ugandan schools (MENISCUS): process evaluation of a pilot intervention study. Pilot Feasibility Stud 6, 51 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40814-020-00585-2
MENISCUS-1 Formative Study
Miiro G, Rutakumwa R, Nakiyingi-Miiro J, Nakuya K, Musoke S, Namakula J, Francis S, Torondel B, Gibson LJ, Ross DA, Weiss HA. Menstrual health and school absenteeism among adolescent girls in Uganda (MENISCUS): a feasibility study. BMC Womens Health. 2018 Jan 3;18(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12905-017-0502-z. PMID: 29298699; PMCID: PMC5753466.
Francis SC, Miiro G, Nakuya K, Rutakumwa R, Nakiyingi-Miiro J, Nabaggala G, Musoke S, Namakula J, Tanton C, Torondel B, Ross DA, Weiss HA; MENISCUS project team. Self-Collection of Vaginal Swabs Among Adolescent Girls in a School-Setting in East Africa. Sex Transm Dis. 2019 May;46(5):335-341. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000990. PMID: 30986795.